The modern healthcare industry relies on a variety of medical gases to support patient care and to enhance the functionality of various medical devices. Among these gases, helium plays a significant role in a multitude of applications, from respiratory treatments to the cooling of equipment. The unassuming helium tank is a fixture in hospitals and clinics, proving that gases are not only essential for life but also for the vitality of the healthcare system.
The Integral Role of Helium in Healthcare
Helium’s unique properties, such as its low boiling point, non-reactivity, and high thermal conductivity, make it indispensable in various medical applications. Because of these characteristics, a helium tank for medical use is a critical supply item for modern healthcare facilities. It aids in a range of diagnostics and treatments that are crucial for patient care.
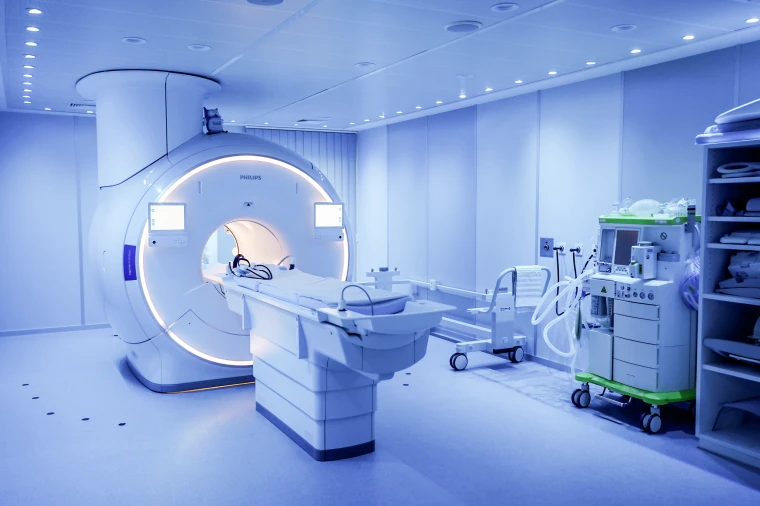
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
One of the most well-known uses of helium in the medical field is in Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). MRI machines utilise helium to cool their superconducting magnets. Without the presence of liquid helium, these magnets would overheat, rendering the MRI machine inoperable. By ensuring the proper cooling of these systems, helium allows for seamless imaging that is vital for accurate diagnoses.
Respiratory Care
Aside from MRI machines, helium is also used in respiratory care. A mixture of helium and oxygen – known as heliox – can support patients experiencing difficulty breathing due to conditions like asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or upper airway obstruction. Heliox’s low density compared to air allows for a more laminar flow of the breathing gas, making it easier for patients to inhale and exhale.
Lab and Scientific Research
In the realm of scientific research, helium plays a role in laboratory procedures. It is used as a carrier gas in gas chromatography, which is essential for separating complex mixtures in chemical analyses. This application is crucial in the pharmaceutical industry for the quality control of medications.
Nitrogen Gas in Medical Settings
Another essential gas that holds significant utility in healthcare is nitrogen. Industrial nitrogen gas serves various purposes, from preservation and packaging of biological specimens to use as a cryogen for the freezing and transportation of cells, tissues, and organs.
Cryopreservation and Cryosurgery
Nitrogen’s cryogenic properties are harnessed for cryopreservation to store biological samples at extremely low temperatures. In cryosurgery, nitrogen is used to freeze and destroy abnormal tissues, such as tumours or warts, whilst minimising damage to surrounding healthy tissues.
Nitrogen as a Calibration Gas
In healthcare facilities, the calibration of medical monitoring devices is paramount. Nitrogen serves as a calibration gas, ensuring that devices like blood gas analysers function correctly and provide accurate readings that are critical for patient care and treatment.
Protection of Medical Compounds
The inert nature of nitrogen makes it the ideal environment for the storage and transport of sensitive medical compounds. It protects these materials from oxidative damage, thereby maintaining their integrity and effectiveness.
Importance of Reliable Gas Supply
Given the essential roles that gases like helium and nitrogen play in healthcare, the consistent and reliable supply of these gases is necessary. And beyond just supply, healthcare providers must ensure that the gases are of the highest purity standards to safeguard against contamination that could affect medical processes or compromise patient safety.
Choosing the Right Gas Supplier
It becomes clear that selecting the appropriate gas supplier is a critical decision for any healthcare facility. The supplier must not only have the capability to deliver gases in the required volumes and purities but also understand the strict regulatory environment of the healthcare industry.
Advanced Gas Technologies
Developments in gas production and storage technologies continue to advance, making it easier for healthcare providers to manage their gas needs efficiently. State-of-the-art tanks and delivery systems have evolved to offer better safety, increased storage capacities, and improved ease-of-use for healthcare personnel.
Conclusion
Medical gases, particularly helium, play a silent yet crucial role in underpinning the operations of modern healthcare facilities. Whether it is through enabling high-level diagnostics like MRI scans or supporting patient care in respiratory treatments, a helium tank is fundamental to the medical industry’s infrastructure.
Much like helium, industrial nitrogen gas demonstrates the versatility and importance of medical gases in varied applications, from cryopreservation to surgical interventions. It is evident that the mastery over these elements—and the technology that harnesses their properties—will continue to shape the landscape of healthcare, contributing to the well-being and recovery of patients around the world.
YOU MAY ALSO LIKE: Exploring V28 Risk Adjustment Model: What Healthcare Providers Must Do Differently